Sikasil® WS-355 N high performance natural stone sealant
Features &Benefits
- 1. Does not stain areas adjacent to the joint
- 2. Meets requirements of ASTM C 920 for Type S, Grade NS, Class 50 (movement capability ± 50 %), ASTM C 1248
- 3. Very good UV and weathering resistance
- 4. Adheres well to natural stone, concrete, glass, metals, coated and painted metals, plastics and wood
Typical Product Data
| Chemical base | 1-component silicone | |
| Color (CQP001-1) | Various colors available A | |
| Cure mechanism | Moisture-curing | |
| Cure type | Neutral | |
| Density (uncured) | 1.3 kg/l
|
|
| Non-sag properties (CQP061-4 / ISO 7390) | Good | |
| Application temperature | ambient
|
5 – 40 °C
|
| Skin time (CQP019-1) | 30 minutes B
|
|
| Tack free time (CQP019-3) | 50 minutes B
|
|
| Curing speed (CQP049-1) | (see diagram) | |
| Shore A hardness (CQP023-1 / ISO 48-4) | 30 C
|
|
| Tensile strength (CQP036-1 / ISO 527) | 1.3 MPa | |
| 100 % modulus (CQP036-1 / ISO 527) | 0.5 MPa | |
| Elongation at break (CQP036-1 / ISO 527) | 550 % | |
| Tear propagation resistance (CQP045-1 / ISO 34) | 3 N/mm | |
| Service temperature | -40 – 150 °C | |
| Shelf life | 12 months D |
| CQP = Corporate Quality Procedure | A) defined by local color chart | B) 23 °C / 50 % r. h. |
| C) after 28 days | D) storage below 25 °C |
Technical Information
CURE MECHANISM
Sikasil® WS-355 N cures by reaction with atmospheric moisture. At low temperatures the water content of the air is generally lower and the curing reaction proceeds somewhat slower (see diagram 1).
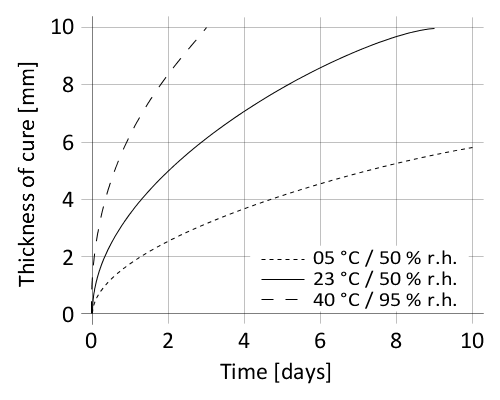
Diagram 1: Curing speed Sikasil® WS-355 N
Applications
Surface preparation
Surfaces must be clean, dry and free from grease, oil and dust. Surface treatment depends on the specific nature of the substrates and is crucial for a long lasting bond.
Application
The optimum temperature for substrate and sealant is between 15 °C and 25 °C.
Sikasil® WS-355 N can be processed with manual, pneumatic or electric driven piston guns.
Joints must be properly dimensioned.
For optimum performance the joint width needs to be designed according to the movement capability of the sealant based on the actual expected movement. The minimum joint depth is 6 mm and a width / depth ratio of minimum 2 : 1 and maximum 4 : 1 must be respected. Joints deeper than 15 mm must be avoided.
For backfilling, it is recommended to use closed cell, sealant compatible foam backer rods e.g. high resilience polyethylene foam rod. If joints are too shallow for backing material to be employed, we recommend using a polyethylene tape. This acts as a release film (bond breaker), allowing the joint to move and the silicone to stretch freely.
Tooling and finishing
Tooling and finishing must be carried out within the skin time of the sealant.
When tooling freshly applied Sikasil® WS-355 N press the sealant to the joint flanks to get a good wetting of the bonding surface. No tooling agents to be used.
Removal
Uncured Sikasil® WS-355 N may be removed from tools and equipment with Sika® Remover-208 or other suitable solvents. Once cured, the material can only be removed mechanically.
Hands and exposed skin have to be washed immediately using hand wipes such as Sika® Cleaner-350H cleaning towels or a suitable industrial hand cleaner and water.
Do not use solvents on skin.
Overpainting
Sikasil® WS-355 N cannot be overpainted.
Application limits
Most Sikasil® WS, SG, IG and WT, silicones manufactured by Sika are compatible with each other.
For specific information regarding compatibility between various Sikasil® products contact the Technical Department of Sika Industry.
To exclude materials influencing Sikasil® WS-355 N, all materials such as gaskets, tapes, setting blocks, sealants, etc., in direct and indirect contact have to be approved by Sika in advance.
Where two or more different reactive sealants are used, allow the first to cure completely before applying the next. Sikasil® WS-355 N may only be used in combination with structural glazing applications after a detailed examination of the corresponding project details.
Do not use Sikasil® WS-355 N on PMMA and PC elements as it may cause environmental stress cracking (crazing).








